
2024 JUPEB Biology questions has been made available here, we also provide answers to the questions. follow the instructions below to have access to your questions and answers.
*JUPEB BIOLOGY*
(2a)
(i) Synecology: The study of the relationships between organisms and their environment in a community or ecosystem.
(ii) Systematics: The scientific study of the classification, identification, and naming of organisms.
(iii) Succession: The gradual and orderly process of change in the composition and structure of an ecological community over time.
(iv) Activation: The process of making a molecule or enzyme chemically active and capable of participating in a biological reaction.
(v) Carrying capacity: The maximum population size of a species that an environment can sustain indefinitely, given the food, habitat, water, and other necessities available in the environment.
(2b)
(PICK ANY THREE)
(i) The cell is the fundamental unit of life.
(ii) All living organisms are composed of one or more cells.
(iii) Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living organisms.
(iv) Cells can only arise from pre-existing cells through the process of cell division.
(v) The activity of an organism depends on the total activity of its constituent cells.
(vi) Energy flows through cells and is conserved by them.
(2c)
(i) Starch: Glycosidic bonds
(ii) Protein: Peptide bonds
(iii) Lipid: Ester bonds
(iv) Nucleic acid: Phosphodiester bonds
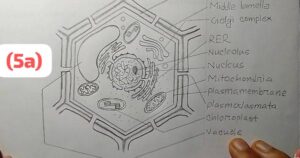
(5a)
Draw the diagram
(5bi)
(PICK ANY FOUR)
(i) Phyllodes
(ii) Spines
(iii) Tendrils
(iv) Scales
(v) Stipules
(vi) Insectivorous leaves
(5bii)
(PICK ANY FOUR)
(i) Thorns
(ii) Tendrils
(iii) Bulbs
(iv) Rhizomes
(v) Tubers
(vi) Cladodes
(5ci)
(PICK ANY TWO)
(i) Cell elongation
(ii) Apical dominance
(iii) Root initiation
(iv) Fruit and seed development
(v) Tropic responses (e.g., phototropism, gravitropism)
(vi) Inhibition of lateral bud growth
(5cii)
(PICK ANY TWO)
(i) Cell division and differentiation
(ii) Delay of senescence (aging) in leaves
(iii) Promotion of shoot formation
(iv) Regulation of nutrient mobilization
(v) Induction of axillary bud break.
(vi) Regulation of root growth and development

Leave a Reply