
NABTEB 2024 Financial Accounting Answers | 2024 Financial 2024 | Sure NABTEB 2024 Financial Obj Answers | 2024 Accounting expo | I Need 2024 Financial Expo
ACCOUNTING OBJ
01-10: DAADBDADCC
11-20: BAACCCADDD
21-30: BBDCABACDD
31-40: CDDBDCDACD
41-50: DABDDAABDC
Completed!!
(1a)
(i) Premises: Asset
(ii) Land and Building: Asset
(iii) Cash: Asset
(iv) Fixtures and Fitting: Asset
(v) Goodwill: Asset
(vi) Debtors for Goods: Asset
(vii) Prepayments: Asset
(viii) Creditors: Liability
(ix) Loan from M. Julianah: Liability
(x) Capital: Neither (Capital represents the owner’s equity in the business, not a liability in the traditional sense)
(1b)
(i) Depletion Method;
The depletion method is used primarily for natural resources such as minerals, oil, and gas. This method allocates the cost of the resource based on the amount extracted during a particular period.
(ii) Revaluation Method;
The revaluation method involves periodically revaluing an asset to its current market value and adjusting the book value accordingly. This method is often used for fixed assets such as property and equipment. The difference between the revalued amount and the current book value is recorded, and depreciation is calculated based on the revalued amount.
(iii) Sum of the Year Digit (SYD) Method;
The Sum of the Year Digit method is an accelerated depreciation method. It calculates depreciation by multiplying the depreciable amount by a fraction that decreases over time. The fraction is determined by dividing the remaining life of the asset by the sum of the years’ digits.
(iv) Retirement and Replacement Method;
This method is used when parts of an asset are periodically retired and replaced. Instead of depreciating the whole asset, depreciation is recorded based on the cost of the parts that are replaced. The cost of the replaced part is expensed, and the new part is capitalized and depreciated over its useful life.
(v) Reducing Balance Method (Declining Balance Method);
The reducing balance method is another form of accelerated depreciation. It applies a constant depreciation rate to the declining book value of the asset each year. The depreciation expense is higher in the earlier years and decreases over time.
(2a)
((i) Direct costs
(ii) Indirect costs
(iii) Fixed costs
(iv) Variable costs
(2b)
(i) Market Value;
Market value refers to the estimated amount for which an asset or a product could be sold on the open market at a given point in time. It represents the price that buyers are willing to pay and sellers are willing to accept under normal conditions, assuming that both parties have adequate information and are not under any undue pressure to make the transaction.
(ii) Prime Cost;
Prime cost is the sum of direct materials and direct labor costs involved in the production of goods. It represents the direct, variable costs that are directly attributable to the manufacturing of the product.
(iii) Profit on Manufacture;
Profit on manufacture is the difference between the total manufacturing costs and the sales value of the manufactured goods. It represents the profit made from the production process itself, before considering any selling, distribution, or administrative expenses.
Number 3

Number 4
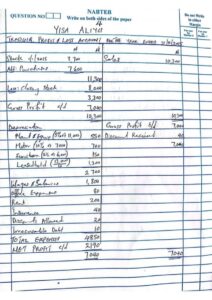
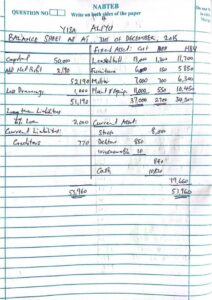
Number 5

Number 6
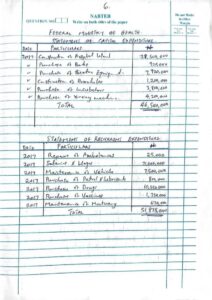
Number 7
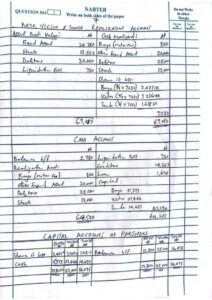
Completed ✅

Leave a Reply