
NABTEB GCE 2024 ECONOMICS Obj & Essays Answers
READ MORE:
🟢 NABTEB GCE 2024 ENGLISH LANGUAGE ANSWERS
🟢 NABTEB GCE 2024 Mathematics Questions & Answers
🟢 NABTEB GCE 2024 Agric Science Obj & Essay Answers
`SECTION B: ANSWER ONE(1) FROM PART I AND FOUR(4) QUESTIONS FROM PART II“`
(1)
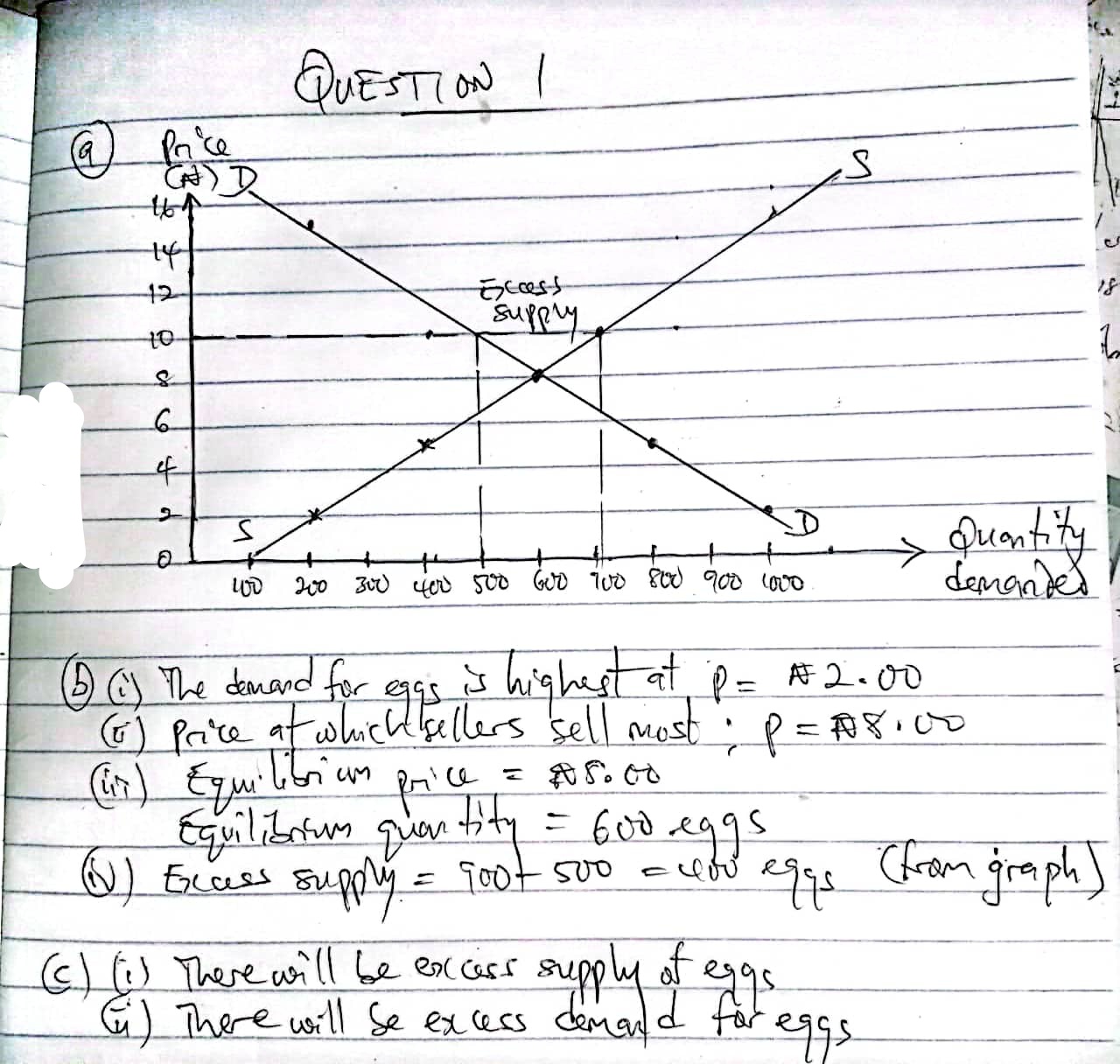
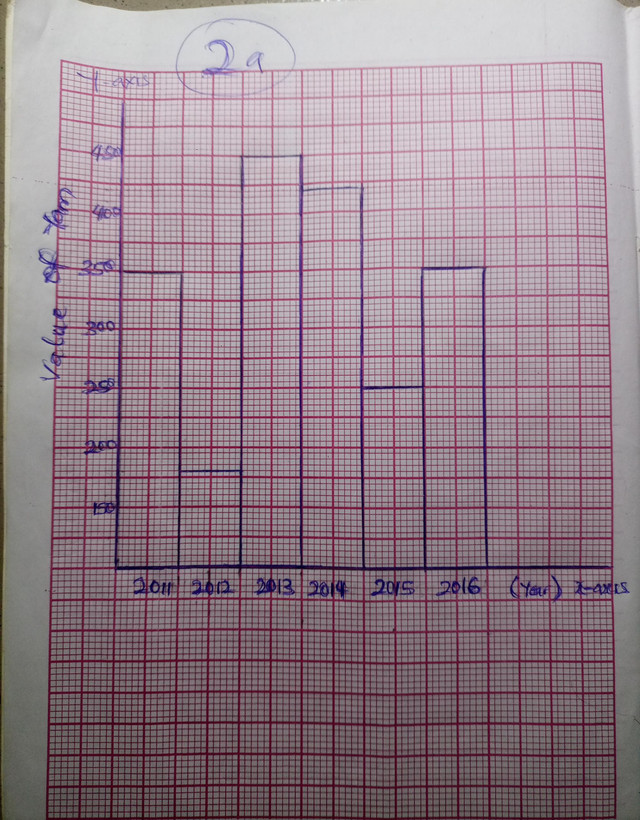
(2a)
(2b)
Range = Maximum value – Minimum value
Range = 450 – 180 = 270
(2c)
SIMILARITIES:
(i) Both use rectangular bars to represent data.
(ii) Both show comparisons among categories.
DIFFERENCES:
(i) In a histogram, bars are adjacent (no gaps) because it represents continuous data. In a bar chart, bars are separated because it represents categorical data.
(ii) The histogram is used for frequency distributions, while the bar chart is used for comparing discrete items.
=======================
(3a)
Overpopulation refers to a situation where the number of individuals in a population exceeds the carrying capacity of their environment, leading to negative consequences for both the population and the environment. This can result from various factors such as increased birth rates, decreased mortality rates, and large-scale migration.
(3b)
(i) Economic Growth: A larger population can lead to increased economic activity as more people contribute to the labor force, driving demand for goods and services. This can stimulate business growth and innovation.
(ii) Increased Workforce: An increasing population provides a larger pool of labor, which can enhance productivity and economic output. A diverse workforce can also bring various skills and ideas, fostering innovation.
(iii) Market Expansion: More people can lead to expanded markets for businesses, allowing companies to grow and potentially leading to lower prices due to economies of scale.
(iv) Cultural Diversity: An increasing population often brings cultural diversity, which can enrich societies through the introduction of new ideas, customs, and practices that enhance social cohesion and creativity.
=======================
(4a)
A chain of distribution refers to the series of steps or processes involved in moving goods from producers to consumers. It encompasses all intermediaries involved in the distribution process, including manufacturers, wholesalers, retailers, and logistics providers. The chain ensures that products reach their final destination efficiently and effectively.
(4b)
(i) Bulk Purchasing: Wholesalers buy large quantities from manufacturers and sell them in smaller quantities to retailers or other businesses, allowing producers to focus on production without worrying about individual sales.
(ii) Storage: They provide storage facilities for goods until they are needed by retailers, helping manage inventory levels and reduce costs related to warehousing for producers.
(iii) Market Information: Wholesalers gather market intelligence about consumer preferences and trends, which they share with manufacturers to help them adjust production strategies.
(iv) Risk Bearing: By purchasing goods in bulk, wholesalers assume the risk of unsold inventory, protecting manufacturers from potential losses due to fluctuations in demand.
(4c)
(i) Cost Reduction: Eliminating wholesalers can reduce distribution costs by cutting out intermediaries, allowing manufacturers to sell directly to consumers or retailers at lower prices.
(ii) Improved Communication: Direct selling can enhance communication between producers and consumers, leading to better understanding of customer needs and quicker response times.
(iii) Increased Profit Margins: Manufacturers may retain a larger share of profits by selling directly without having to share margins with wholesalers.
(iv) Streamlined Distribution: Removing wholesalers can simplify the supply chain, reducing complexity and improving efficiency in getting products to market.
=======================
(5a)
Specialisation refers to the process by which individuals, businesses, or countries focus on producing a limited range of goods or services in which they have a particular expertise or efficiency. By concentrating on one or a few tasks, producers can increase productivity and improve efficiency.

Leave a Reply