
Nabteb computer Craft Studies | what is computer Craft Studies | computer Craft Studies | Computer Craft practical | Computer Craft Obj & essays
READ THIS 2023 NABTEB Computer Craft Studies Obj & Essay Legit Expo – June/july
COMPUTER CRAFT OBJ
01-10: DADBAAACBA
11-20: BDDBDBDDDA
21-30: BCCABCCCCB
31-40: CCBACBACDB
COMPLETED
“`ANSWER FIVE(5) QUESTIONS ONLY“`
(1a)
(i) Band: A range of frequencies or wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum, divided into separate categories for various applications.
(ii) Bandwidth: The width of a frequency range, measured in hertz (Hz), that a signal occupies or a system can transmit.
(iii) Frequency: The number of oscillations or cycles per second of a wave, measured in hertz (Hz).
(iv) Channel: A designated frequency range or band used for communication, data transmission, or broadcasting.
(1b)
Radiowave wireless transmission:
Radio waves are used to transmit signals wirelessly through the air, using a transmitter to modulate the signal onto a carrier wave, which is then received by a receiver that demodulates the signal.
Frequency bands:
(i) VHF (Very High Frequency) band
(ii) UHF (Ultra High Frequency) band
≠===≠================≠=======
(2a)
(i) Centralized Data Processing System:
In a centralized system, all data processing occurs in a single location, typically a mainframe computer or a server. All input data is sent to this central location for processing, and the processed data is then distributed to various locations. This approach concentrates resources and control in one place, making it easier to manage and maintain.
(ii) Decentralized Data Processing System:
A decentralized system distributes data processing across multiple locations, each with its processing capabilities. Each location processes its data, and the processed data may be shared with other locations as needed. This approach allows for more autonomy and flexibility at each location.
(iii) Distributed Data Processing System:
A distributed system spreads data processing across multiple machines or nodes, connected through communication networks. Each node processes its own data and shares results with other nodes as needed. This approach enables scalability, fault tolerance, and improved processing power, as nodes can work together to achieve a common goal.
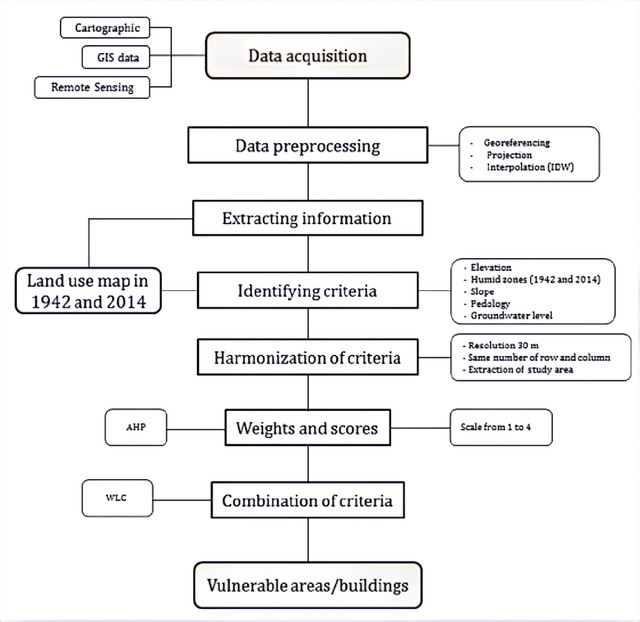
(2b)
Draw the diagram
≠===≠================≠=======
(3a)
(i) Password:
A password is a secret sequence of characters used to authenticate a user’s identity, granting access to a computer system, network, or application.
(ii) Encryption:
Encryption is the process of converting plaintext data into unreadable ciphertext to protect it from unauthorized access. Only those with the decryption key or password can access the encrypted data.
(3b)
(i) Sequential Access:
Sequential access refers to a data access method where data is processed in a sequential order, one record after another. Examples include magnetic tapes and serial processing.
(ii) Direct Access:
Direct access, also known as random access, allows data to be accessed directly and immediately, without sequential processing. Examples include hard disk drives and RAM.
(iii) Serial Access:
Serial access refers to data transfer or processing one bit or character at a time, in a sequential manner. Examples include serial ports and serial communication protocols.
(iv) Indexed Sequential Access:
Indexed sequential access combines sequential access with indexing, allowing for faster data retrieval. An index is created to point to specific data locations, enabling direct access to specific records.
≠===≠================≠=======
(4a)
A presentation is a visual communication tool used to convey information, ideas, or messages to an audience, often consisting of a series of slides, images, text, and other multimedia elements.
(4b)
(i) Themes:
In PowerPoint, themes are pre-designed templates that define the visual style, layout, and formatting of a presentation, including colours, fonts, and graphics.
(ii) Slide Tab:
The Slide Tab is a navigation tab in the PowerPoint ribbon that allows users to view and manage individual slides, including adding, deleting, and rearranging slides.
(iii) Slide Pane:
The Slide Pane is the main workspace in PowerPoint where users can view and edit the current slide, adding text, images, and other content.
(v) Master:
In PowerPoint, a Master is a template that controls the overall design and layout of a presentation, including the slide layout, theme, and formatting. There are two types of Masters: Slide Master and Theme Master.
(4c)
(i) Print Slides
(ii) Print Handouts
≠===≠================≠=======
(5a)
(i)
A spreadsheet is a software application that enables
users to store, organize, and analyze data in a table
format, with rows and columns, and perform
calculations and visualizations.
(ii)
The Formula Bar is a toolbar in a spreadsheet
application that displays the current cell’s contents,
allowing users to edit and enter formulas, functions,
and data.
(iii)
The Name Box is a toolbar in a spreadsheet
application that displays the name of the currently
selected cell or range and allows users to define
names for cells or ranges.
(iv)
A Sheet Tab is a tab in a spreadsheet application that
represents an individual worksheet or spreadsheet
and allows users to switch between different sheets
in a workbook.
(5bi)
(i) Column Chart
(ii) Line Chart
(iii) Pie Chart
(iv) Bar Chart
(v) Area Chart
(vi) Scatter Chart
(5bii)
(i) Microsoft Excel
(ii) Google Sheets
••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••
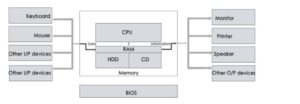
(6a)
Draw the diagram
(6b)
(i) Control Unit (CU): Retrieves and decodes
instructions, manages data flow, and controls overall
operations.
(ii) Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU): Performs arithmetic
and logical operations, such as addition, subtraction,
AND, OR, etc.
(iii) Registers: Small amount of on-chip memory that
stores data temporarily while it’s being processed.
(iv) Bus: A communication pathway that allows
different components to exchange data.
(6c)
Hard Disk is a non-volatile storage device that uses
spinning disks and mechanical heads to read and
write data, offering higher storage capacity but
slower access times. It is more prone to mechanical
failure. On the other hand, Flash Disk, also known as
Solid-State Drive (SSD), is a non-volatile storage
device that uses flash memory to store data,
providing faster access times but lower storage
capacity. It is more durable and resistant to physical
shock.
••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••
(7a)
(i) Bit:
A bit (short for binary digit) is the smallest unit of
data in a computer, representing a single binary
value, either 0 or 1.
(ii) Nibble:
A nibble is a group of four bits. It is half of a byte
and can represent 16 different values (from 0000 to
1111 in binary).
(iii) Byte:
A byte consists of eight bits. It is a standard unit of
data used to represent a single character of text in
most computer systems.
(iv) Word:
A word is a fixed-sized group of bits handled as a
unit by the processor. The size of a word is typically
the number of bits the CPU processes at one time,
commonly 16, 32, or 64 bits.
(7b)
(i) Digital Computer:
A digital computer processes data in binary form (0s
and 1s). It performs calculations and logical
operations using digital signals and is used for tasks

Leave a Reply