
NECO AGRIC. SCIENCE
2024 NECO AGRIC SCIENCE
01-10: CADBDBEDBA
11-20: EADDADACAC
21-30: CCAEADADDE
31-40: BBACCCDBCD
41-50: AACEDAADAC
51-60: EEDACEBDAC
COMPLETED
✅✅✅✅
(1a)
(PICK ANY FIVE)
(i) Agriculture is the primary source of employment in Nigeria, employing about 70% of the labor force.
(ii) It provides food for the increasing population, ensuring food security.
(iii) Agriculture supplies raw materials to industries, such as cotton for the textile industry and cocoa for the confectionery industry.
(iv) Export of agricultural products like cocoa, palm oil, and rubber provides foreign exchange earnings.
(v) Agriculture fosters rural development through the provision of infrastructure like roads, schools, and healthcare facilities.
(vi) The agricultural sector contributes significantly to the national GDP and government revenue through taxes and exports.
(vii) Agriculture helps diversify the economy, reducing dependence on the oil sector.
(1bi) Inconsistent government policies:
(PICK ANY THREE)
(i) Establishing a consistent agricultural policy framework that is resistant to frequent changes by successive governments.
(ii) Involving all stakeholders in policy formulation to ensure that policies are realistic and implementable.
(iii) Setting up mechanisms for regular monitoring and evaluation of agricultural policies to ensure they are effectively implemented and adjusted as needed.
(iv) Providing incentives for policy adherence and discouraging abrupt policy changes.
(1bii) Unpredictable climate:
(PICK ANY THREE)
(i) Developing and promoting the use of climate-resilient crop varieties that can withstand extreme weather conditions.
(ii) Investing in irrigation infrastructure to reduce dependence on rain-fed agriculture.
(iii) Enhancing weather forecasting and early warning systems to help farmers make informed decisions.
(iv) Promoting sustainable agricultural practices that can mitigate the effects of climate change.
(1c)
(PICK ANY FIVE)
(i) Tree pullers can selectively remove trees without disturbing other vegetation.
(ii) They can pull out entire trees, including roots, reducing the chances of regrowth.
(iii) Tree pullers cause less soil disturbance compared to bulldozers, preserving soil structure and fertility.
(iv) They are generally more cost-effective for small to medium-scale land clearing operations.
(v) Tree pullers have a lower environmental impact, causing less destruction to the ecosystem compared to bulldozers.
(vi) They are often more efficient in terms of time and labor for clearing smaller areas.
(vii) Less disturbance to the soil helps in preserving beneficial soil microorganisms
*NECO AGRIC. SCIENCE*
(2ai)
(PICK ANY ONE)
Farm planning is the process of organizing and allocating farm resources, such as land, labor, and capital, to achieve maximum efficiency and productivity in farming operations.
OR
Farm planning is a decision making process in the farm business, which involves organization and management of limited resources to realize the specified goals continuously.
OR
Farm Planning is the process of organizing and managing farm resources and operations to achieve specific goals and objectives.
(2aii)
(i) Gunter’s chain – Measuring distance
(ii) Theodolite – Measuring horizontal and vertical angles
(iii) Beacon – Marking survey points
(iv) Prismatic compass – Measuring bearings and angles
(2b)
(PICK ANY FIVE)
(i) Science and technology have led to the development of improved crop varieties with higher yields and resistance to pests and diseases.
(ii) The introduction of machinery like tractors, harvesters, and planters has increased farming efficiency and productivity.
(iii) Technologies such as GPS and remote sensing have enabled precision agriculture, optimizing input use and improving yields.
(iv) Biotechnology and chemical research have provided effective pest and disease control measures.
(v) Advances in storage and processing technologies have reduced post-harvest losses and improved the quality of agricultural products.
(vi) Soil Health Monitoring: Technology allows for better monitoring and management of soil health, ensuring sustainable farming practices.
(vii) Digital platforms have enhanced agricultural extension services, providing farmers with access to vital information and resources
(2c)
(PICK ANY FIVE)
(i) Agriculture provides raw materials for agro-allied industries, such as fruits for juice production.
(ii) Both sectors provide employment opportunities, contributing to economic development.
(iii) Agro-allied industries create markets for agricultural products, adding value to them.
(iv) Collaboration between the two sectors fosters innovation and research, leading to improved agricultural practices and products.
(v) The growth of agro-allied industries stimulates agricultural development and vice versa, creating a symbiotic relationship that drives economic growth.
(vi) Agro-allied industries add value to agricultural products, increasing their marketability and profitability.
(vii) The growth of agro-allied industries often leads to the development of infrastructure such as roads, storage facilities, and processing plants.
*NECO AGRIC. SCIENCE*
(3a)
(i) Soil pH:
Soil pH affects the availability of nutrients to plants and the activity of soil microorganisms. For example, a very acidic soil (low pH) can lead to nutrient deficiencies or toxicities, hindering plant growth.
(ii) Soil Structure:
Soil structure refers to the arrangement of soil particles into aggregates. Good soil structure improves aeration, water infiltration, and root penetration, enhancing plant growth. Poor soil structure can lead to compaction, reducing root growth and water movement.
(iii) Topography:
Topography influences drainage, erosion, and the microclimate of an area. Steep slopes can lead to erosion and loss of topsoil, while flat areas may have poor drainage, affecting crop yield.
(3b)
(PICK ANY FOUR)
(i) Rocks weather over time to form soil, which is the medium for plant growth.
(ii) Rocks release essential minerals and nutrients into the soil as they break down.
(iii) Rocks are used in constructing agricultural infrastructure like farm buildings and roads.
(iv) Certain types of rocks help in retaining moisture in the soil, beneficial for crop growth.
(v) Rocks can be used to create terraces on hilly terrain, reducing soil erosion and improving arable land.
(3c)
(PICK ANY THREE)
(i) Nitrogen, particularly in the nitrate form, can be leached away from the soil profile by percolating water.
(ii) Microbial processes in waterlogged soils convert nitrates to nitrogen gas, which is lost to the atmosphere.
(iii) Ammonia from fertilizers can volatilize and be lost to the atmosphere, especially in alkaline soils.
(iv) Nitrogen is taken up by crops and removed from the soil when the crops are harvested.
(3d)
(PICK ANY THREE)
(i) Pesticides
(ii) Herbicides
(ii) Heavy metals
(iii) Plastics
(iv) Industrial chemicals
(v) Petroleum products
(vi) Agricultural runoff
(vii) Sewage and wastewater
*NECO AGRIC. SCIENCE*
(4ai)
PICK ANY ONE
Irrigation is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow crops, landscape plants, and lawns.
OR
Irrigation is the artificial application of water to the soil to assist in the growth of crops.
(4aii)
(PICK ANY FOUR)
(i) Excessive irrigation can lead to waterlogged soils, reducing oxygen availability to roots.
(ii) Over-irrigation, especially in arid areas, can lead to the accumulation of salts in the soil, affecting crop growth.
(iii) The infrastructure and energy required for irrigation can be expensive, limiting its accessibility.
(iv) Intensive irrigation can deplete local water resources, affecting other uses and ecosystems.
(v) Improper irrigation practices can lead to soil erosion, reducing soil fertility.
(vi) Irrigation can create standing water, which can become breeding grounds for mosquitoes and other disease vectors.
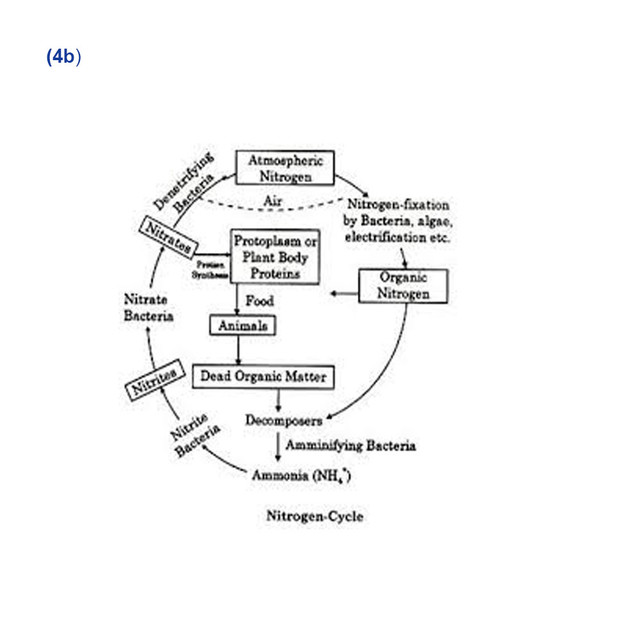
(4b)
(4c)
(PICK ANY THREE)
(i) Metamorphic rocks are generally harder and more resistant to weathering than their original forms due to recrystallization.
(ii) Many metamorphic rocks have a banded or foliated texture, where minerals are aligned in planes.
(iii) Metamorphic rocks often undergo recrystallization, forming new mineral structures without melting.
(iv) Metamorphic rocks often have a higher density than the original rocks due to the pressure they were subjected to during formation.
(v) Metamorphic rocks contain minerals that are stable under high pressure and temperature conditions
(4c)
(PICK ANY TWO)
(i) Limestone
(ii) Gypsum
(iii) Halite (rock salt)
(iv) Chert
(v) Dolomite
(5a)
(i) Soil requirement: Rubber trees thrive best in well-drained, deep, loamy soils rich in organic matter with good water retention capacity and a pH range of 4.5 to 6.5.
(ii) Climatic requirement: Rubber trees require a hot, humid climate with consistent rainfall ranging from 2000 to 3000 mm annually. They thrive in temperatures between 25°C and 35°C and need a frost-free environment.
(iii) Planting date in nursery: Rubber seeds are typically sown in the nursery at the beginning of the rainy season, which ensures adequate moisture for germination. This period varies by region but generally falls between May and July.
(iv) One fungal disease: Powdery mildew is a common fungal disease affecting rubber trees.
(v) One industrial product: Natural rubber is a significant industrial product derived from rubber trees.
(5bi)
(PICK ANY FOUR)
(i) Reduced crop yield
(ii) Increased susceptibility to diseases
(iii) Poor growth and development
(iv) Low-quality produce
(v) Increased pest infestation
(vi) Higher cost of production due to additional inputs required
(5bii)
(PICK ANY TWO)
(i) Use healthy and disease-free parent plants
(ii) Ensure the layering medium is moist but well-drained
(iii) Avoid damaging the stem during the process
(iv) Protect the layered part from pests and harsh environmental conditions
(5c)
(PICK ANY FIVE)
(i) High nutritional value
(ii) Good palatability for livestock
(iii) Resistance to pests and diseases
(iv) Adaptability to local climate and soil conditions
(v) High yield potential
(vi) Persistent growth throughout the grazing season
(vii) Ability to recover quickly after grazing
(6a)
(PICK ANY ONE)
Agroforestry is a land use management system in which trees or shrubs are grown around or among crops or pastureland.
OR
Agroforestry is a land management system that integrates trees and shrubs into agricultural landscapes to create environmental, economic, and social benefits.
(6b)
(PICK ANY FOUR)
(i) It is used in enhancing aesthetic appeal of landscapes
(ii) It provides shade and reduces heat
(iii) It is used in improving air quality by absorbing pollutants
(iv) It serves as windbreaks and reduces wind erosion
(v) It attracts beneficial insects and pollinators
(vi) It provides recreational spaces for people
(6c)
(PICK ANY FOUR)
(i) It reduces crop yields through direct feeding damage
(ii) It increases production costs due to pest control measures
(iii) It spreads plant diseases that can devastate crops
(iv) It reduces the quality of harvested produce
(v) It leads to market restrictions and trade barriers due to pest infestations
(vi) It necessitates the development and use of resistant crop varieties
(6d)
(i) Causal organism: Swollen shoot disease of cocoa is caused by the Cacao swollen shoot virus (CSSV).
(ii) One symptom: One symptom of swollen shoot disease is the swelling of shoots and veins on leaves, accompanied by leaf discoloration and stunted growth.
(iii) One mode of transmission: The disease is primarily transmitted by mealybugs, which transfer the virus as they feed on the sap of infected plants.
(iv) One control measure: One control measure is the removal and destruction of infected plants to prevent the spread of the virus to healthy plants.
(6e)
(PICK ANY TWO)
(i) Crop rotation to disrupt weed life cycles
(ii) Mulching to suppress weed growth
(iii) Manual weeding or hoeing to remove weeds
(iv) Planting cover crops to outcompete weeds
(7a)
(PICK ANY FOUR)
(i) Reduced egg production
(ii) Lower egg quality, such as thinner shells
(iii) Decreased feed intake by hens
(iv) Increased water consumption
(v) Higher mortality rates among hens
(vi) Increased incidence of heat stress and related illnesses
(7b)
(PICK ANY THREE)
(i) Collection and cleaning of bones
(ii) Boiling or steaming bones to remove fat and soft tissues
(iii) Crushing or grinding the cleaned bones into smaller pieces
(iv) Acid treatment to dissolve the mineral content
(v) Drying and milling the treated bones into fine powder
(7c)
(PICK ANY FIVE)
(i) Regular cleaning of the pond
(ii) Monitoring and maintaining water quality
(iii) Feeding fish with appropriate diets
(iv) Controlling aquatic weeds and algae
(v) Preventing and treating fish diseases
(vi) Regularly removing debris and waste
(vii) Ensuring proper aeration and oxygen levels
(7d)
(PICK ANY FOUR)
(i) Maintaining good hygiene and sanitation
(ii) Implementing vaccination programs
(iii) Isolating and quarantining sick animals
(iv) Regular veterinary check-ups and health monitoring
(v) Providing balanced and nutritious diets
(vi) Proper waste management and disposal
(8a)
(PICK ANY FOUR)
(i) Swelling and relaxation of the vulva
(ii) Secretion of colostrum from the udder
(iii) Restlessness and frequent lying down and getting up
(iv) Nesting behavior and seeking a secluded area
(v) Increased vocalization
(vi) Contractions and visible abdominal straining
(8b)
(PICK ANY THREE)
(i) Reduced growth rate and weight gain
(ii) Decreased egg production
(iii) Irritation and constant scratching
(iv) Feather damage and loss
(v) Increased susceptibility to secondary infections
(8c)
(i) Causal organism: Foot and Mouth Disease is caused by the Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus (FMDV).
(ii) One symptom: The formation of blisters on the mouth, snout, and feet.
(iii) One mode of transmission: The disease can be transmitted through direct contact with infected animals, contaminated equipment, and feed.
(iv) One control measure: Implementation of strict biosecurity measures, including quarantine and movement restrictions of infected and at-risk animals.
(8d)
(PICK ANY TWO)
(i) Artificial vagina
(ii) Electroejaculation
(iii) Manual stimulation
(iv) Collection from mated females
(8e)
(PICK ANY THREE)
(i) Controlled stocking: This is a case whereby the correct number of animals are allowed to graze at a particular area of rangeland in order not to be exhausted.
(ii) Reseeding: It involves replanting of forage crops on a bald land where farm animals have grazed a lot on a rangeland, reseeding becomes necessary.
(iii) Use of fertilizer application: Fertilizer is needed to be applied to ensure enough foliage formation. Eg NPK.
(iv) Paddocking: Here rangeland should be divided into smaller units and the animals will graze on them in circular manner unit by unit. This ensues the regrowth of the rangeland. Sometimes, farmers may cut forage for hay and silage from the resting rangeland.
(v) Irrigation: Rangeland should be irrigated during dry season to maintain continuous supplying of forage crops year in year out etc.
(9a)
(PICK ANY THREE)
(i) Economic Growth: Entrepreneurship in agriculture stimulates economic development by creating jobs, increasing productivity, and contributing to GDP.
(ii) Innovation: Agricultural entrepreneurs introduce new technologies and practices, enhancing efficiency and sustainability in farming.
(iii) Rural Development: It promotes rural development by generating income, improving infrastructure, and raising the standard of living in rural areas.
(iv) Food Security: Entrepreneurial ventures in agriculture help ensure a stable supply of food by enhancing production and distribution.
(v) Diversification: Entrepreneurship allows for the diversification of agricultural activities, reducing dependency on a single crop and spreading risk.
(9b)
(i) Assets
(ii) Liabilities
(9c)
(PICK ANY FIVE)
(i) Enhancing the efficiency and output of agricultural activities.
(ii) Facilitating the adoption of modern farming techniques and technologies.
(iii) Providing training and education to farmers on best practices and innovations.
(iv) Assisting farmers in finding markets and improving their marketing strategies.
(v) Promoting environmentally friendly and sustainable farming methods.
(vi) Reducing poverty in rural areas through improved agricultural practices and income generation.
(vii) Supporting the overall development of rural communities through agricultural advancement.
(9d)
(PICK ANY THREE)
=PLEASE TABULATE=
Group Method:
(i) Small, specific groups of farmers
(ii) High level of interaction and personal engagement
(iii) Immediate and direct feedback
(iv) Flexible and can be adjusted based on group dynamics
(v) Easier to monitor and evaluate impact on participants
Mass Method:
(i) Large, general population of farmers
(ii) Low level of interaction, often one-way
(iii) Delayed or limited feedback
(iv) Fixed content, less flexible
(v) Difficult to monitor and evaluate impact on individuals
(10a)
(PICK ANY FIVE)
(i) Limited skilled labour
(ii) Pest and disease management
(iii) Weather and climate cChange
(iv) Market Fluctuations
(v) Resource Management
(vi) Regulatory Compliance
(vii) Financial Constraints
(vi) Equipment Maintenance
(10b)
(PICK ANY FOUR)
(i) It helps in identifying market needs, trends, and opportunities.
(ii) It helps in creating products that meet market demands.
(iii) Marketing locates areas of surplus production and relocates the produce to areas of shortages.
(iv) It provides income from export trade and also provides foreign exchange for import of agricultural machines.
(v) Marketing ensures the availability of seasonal produce at off season.
(vi) It encourages or motivates farmers to produce more.
(10c)
(PICK ANY THREE)
(i) The production risk
(ii) The market risk
(iii) Financial Risk
(iv) Environmental Risk
(v) Operational risk
(10d)
(PICK ANY FOUR)
(i) Farmers can see and understand new techniques and practices in action.
(ii) It provides practical, hands-on learning opportunities.
(iii) It allows for real-time questions and answers, clarifying doubts.
(iv) It engages farmers more effectively than lectures or written materials.
(v) It boosts farmers’ confidence in adopting new practices by seeing successful examples.
(vi) It increases the likelihood of adoption of new techniques by showing tangible benefits.

Leave a Reply