
WAEC 2024 GEOGRAPHY | GEOGRAPHY RUNS | GEOGRAPHY EXPO | 2024 GEOGRAPHY EXPO ANSWERS | SURE GEOGRAPHY EXPO ANSWERS | HOW TO PASS GEOGRAPHY EXPO | GEOGRAPHY OBJ | GEOGRAPHY 2024 ESSAY
GEOGRAPHY OBJ
01-10: BADBCCADDC
11-20: ACCAACBBCC
21-30: BCABCAABAD
31-40: ABBACAACAC
41-50: CBADABBDBB
Completed ✅
(1a)
(i)Primary industries are involved in the extraction and production of raw materials from the earth. WHILE Secondary industries are concerned with processing raw materials obtained from primary industries into finished or semi-finished goods.
(ii)Primary industries include agriculture, mining, forestry, fishing, and other activities that harvest natural resources. WHILE Secondary industries involve manufacturing and construction activities.
(iii)Primary Industries adds less value to products as they are raw materials, usually sold at lower prices. WHILE Secondary Industries adds significant value through processing and manufacturing, resulting in higher-priced goods.
(iv)Primary Industries relies on traditional skills and labor-intensive methods, requiring less specialized training. WHILE Secondary Industries requires more technical skills and specialized training for complex machinery and production processes.
(1b)
(PICK ANY FOUR)
(i)Light industries typically require less capital investment compared to heavy industries
(ii)Light industries often produce consumer goods that can be sold in local or regional markets, reducing the need for expensive transportation infrastructure.
(iii)Light industries can adapt quickly to changing market demands and can be scaled up or down more easily than heavy industries
(iv)Light industries generally have a smaller environmental footprint compared to heavy industries, making them more acceptable in regions with less stringent environmental regulations
(v)Developing countries usually have a large supply of labour willing to work for lower wages, which is suitable for labour-intensive light industries such as textiles and apparel manufacturing.
(1c)
(PICK ANY FOUR)
(i)Employment Generation:The industrial sector creates numerous job opportunities, which helps reduce unemployment and underemployment, improving the standard of living.
(ii)Income Generation: Industrial activities contribute to the gross domestic product (GDP) and national income through the production of goods and services, leading to higher national revenue
(iii)Technological Advancement: Industrialization encourages technological innovation and the adoption of new technologies, which can enhance productivity and efficiency across various sectors of the economy.
(iv)Infrastructure Development: The growth of industries often leads to the development of infrastructure such as roads, ports, power supply, and communication networks, which benefits the broader economy.
(v)Diversification of the Economy: A robust industrial sector reduces dependency on agriculture or a single natural resource, diversifying the economic base and making the economy more resilient to external shocks.
(2a)
(PICK ANY FOUR)
(i)Rural to Urban Migration
(ii)Urban to Rural Migration
(iii)International Migration
(iv)Seasonal Migration
(v)Internal Migration
(vi)Forced Migration
(2b)
(PICK ANY FIVE)
(i)Economic Opportunities: People move in search of better employment prospects and higher wages, often migrating from rural areas to urban centers.
(ii)Education: Access to better educational facilities can drive families to relocate to areas with schools and universities.
(iii)Conflict and Insecurity: Armed conflicts, political instability, and violence can force people to flee their homes for safer regions or countries.
(iv)Environmental Factors: Natural disasters, climate change, and degradation of arable land can push people to migrate to more hospitable areas.
(v)Healthcare Access: Availability of better healthcare services can attract people to move to regions with hospitals and clinics.
(vi)Government Policies and Development Projects: Infrastructure development, land reforms, and resettlement programs initiated by governments can lead to population movement
(vii)Social and Cultural Factors: social and cultural factors is also part of factor that trigger population movement in Tropical Africa. Family reunification, marriage, and cultural ties can influence people to migrate
(2c)
(PICK ANY THREE)
(i)Economic Growth: An influx of migrants can boost local economies by providing labor, increasing consumer demand, and stimulating business activities.
(ii)Urbanization: Rapid population movement to urban areas can lead to the expansion of cities and the development of new urban centers.
(iii)Pressure on Services and Infrastructure: Increased population can strain existing services such as healthcare, education, housing, and transportation infrastructure
(iv)Cultural Diversity: Migration introduces new cultural practices, languages, and traditions, enriching the social fabric of the destination region.
(v)Environmental Impact: Higher population densities can lead to environmental degradation, including deforestation, water pollution, and increased waste production.
SEE THIS; WAEC 2023 Results Testimonies By Gidiclass – Click Here
(3a)
(PICK ANY ONE)
The birth rate is the number of live births per 1,000 people in a given population over a specific period, typically one year. It is an essential demographic indicator used to assess population growth and reproductive health trends.
OR
The birth rate is a demographic indicator that measures the frequency of live births in a specified population, expressed as the number of live births per 1,000 people in that population over the course of one year.
(3b)
(PICK ANY THREE)
(i) Cultural Practices: In many parts of Tropical Africa, cultural norms and traditions favor large families. High value is placed on having many children, which can increase the birth rate.
(ii) Economic Factors: In agrarian societies, children are often seen as economic assets who can contribute to the family’s labor force. This economic benefit can drive higher birth rates.
(iii) Access to Education: Lower levels of education, particularly among women, often correlate with higher birth rates. Educated women tend to have fewer children as they have greater access to family planning information and career opportunities.
(iv) Health Care Accessibility: Limited access to healthcare, including reproductive health services and contraception, can result in higher birth rates.
(v) Government Policies: Policies that promote or discourage family planning can significantly impact birth rates. In some areas, lack of support for family planning services can lead to higher birth rates.
(3c)
(PICK ANY THREE)
(i) Labor Force: A large population provides a substantial labor force, which can drive economic development if properly harnessed.
(ii) Market Size: Over-population can lead to a large domestic market, encouraging businesses to invest and thrive due to high demand for goods and services.
(iii) Innovation and Cultural Diversity: A diverse and large population can foster innovation and cultural richness, contributing to a dynamic and creative society.
(iv) Military Strength: A larger population can translate into a stronger military force, which may enhance national security.
(v) Human Resources: Over-population can provide a wealth of human resources, which can be advantageous for various sectors such as education, healthcare, and technology.
(3d)
(PICK ANY THREE)
(i) Resource Depletion: Over-population puts immense pressure on natural resources, leading to depletion and environmental degradation.
(ii) Unemployment: High population growth can result in insufficient job opportunities, leading to high levels of unemployment and underemployment.
(iii) Poor Living Conditions: Over-population can strain infrastructure and social services, resulting in overcrowded living conditions, inadequate housing, and poor sanitation.
(iv) Healthcare Strain: Over-population can overwhelm healthcare systems, making it difficult to provide adequate medical services to everyone.
(v) Food Security: High population growth can lead to food shortages and increased malnutrition as the demand for food outpaces supply.
No 4
(5a)
(PICK ANY FIVE)
(i) Climate: Different regions in Nigeria have varying climatic conditions, which affect what crops can be grown. For instance, the northern region with its arid climate is suitable for crops like millet and sorghum, while the southern region with its humid climate supports crops like cocoa and palm oil.
(ii) Soil Type:The fertility and type of soil in different parts of Nigeria influence agricultural productivity. Areas with rich, loamy soil are more suitable for crop farming, while regions with poor, sandy soil may be better for certain types of grazing.
(iii) Topography: The physical landscape, including mountains, valleys, and plains, affects what can be produced. Flat plains are ideal for large-scale farming, while hilly or mountainous areas may be better for specific crops or livestock.
(iv) Water Availability: Access to water resources, such as rivers, lakes, and rainfall, is crucial for agriculture and other production activities. Areas with abundant water resources can support irrigation-based agriculture and industries that require significant water input.
(v) Economic Factors: Market demand, availability of capital, and access to technology can influence production. Regions with better infrastructure and market access can support more diverse and technologically advanced production.
(vi) Government Policies: Policies such as subsidies, tariffs, and support for certain industries can encourage the production of specific goods. For example, government incentives for agricultural production can boost farming activities.
(vi) Human Resources: The availability of skilled and unskilled labor affects what can be produced. Areas with a higher population and better educational facilities can support industries requiring specialized skills.
(5b)
(PICK ANY FIVE)
(i) Poor Infrastructure: Inadequate transportation networks, such as roads, railways, and ports, can impede the movement of goods within the country and for export, leading to delays and increased costs.
(ii) Corruption: Corruption at various levels of government and within trade-related institutions can create obstacles for businesses, including the need to pay bribes and deal with bureaucratic red tape.
(iii) Insecurity: Issues such as terrorism, banditry, and piracy can disrupt trade routes, lead to loss of goods, and deter both local and foreign investors from engaging in trade activities.
(iv) Inconsistent Government Policies: Frequent changes in trade policies, tariffs, and regulations can create uncertainty and instability, making it difficult for businesses to plan and operate effectively.
(v) Lack of Access to Finance: Difficulty in obtaining loans and other financial services can hinder businesses from expanding their operations and engaging in larger-scale trade.
(vi) Electricity Shortages: Frequent power outages and lack of reliable electricity supply can affect production processes, increase costs, and reduce the competitiveness of Nigerian goods in the international market.
(vii) Trade Barriers: High tariffs, import/export restrictions, and complex customs procedures can make it difficult for businesses to trade across borders, reducing trade volumes and increasing costs.
CHECK THIS; WAEC 2024 SSCE Examination Timetable – MAY/JUNE
(6a)
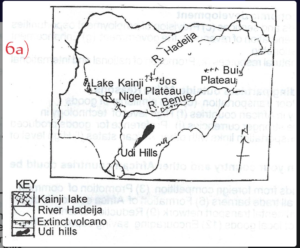
(i) Longitude 15°E: (Shown as a vertical line on the map)
(ii) Udi Hill: (Located in Enugu State)
(iii) Lokoja: (Located in Kogi State)
(6b)
(i)Agricultural production: Highlands provide suitable terrain for farming and crop production.
(ii)Water source: Highlands are sources of rivers and streams, providing water for irrigation and drinking.
(iii)Tourism and recreation: Highlands offer scenic views and opportunities for hiking and outdoor activities.
(6c)
(i)Inadequate infrastructure: The presence of highlands in Nigeria makes it difficult to construct infrastructure, such as roads and bridges, which are necessary for transportation and communication
(ii)Soil erosion: The steep slopes of highlands make them prone to soil erosion, which can lead to desertification and loss of arable land.
(iii)Inaccessibility: Highland areas may be difficult to access, which can limit economic opportunities and impede development.
(iv)Marginalization: People living in highland areas may be marginalized and excluded from development opportunities, leading to poverty and socio-economic inequality.

Leave a Reply