
NABTEB 2024 BRICKLAYING/ BLOCKLAYING AND CONCRETING ANSWERS
BRICK/BLOCK & CONCRETING
01-10: DCBAABCCCD
11-20: BADCDDCAAD
21-30: ABCABCDCAC
31-40: DDCCACDABC
READ MORE;
NABTEB Government Answers For Essay & Obj 2024
NABTEB 2024 Carpentry & Joinery Answers
NABTEB Commerce 2024 Answers ( Obj & Essays)
NABTEB Computer Craft Studies 2024 Obj & Essay Answers
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
“`ANSWER FIVE(5) QUESTIONS ONLY“`
(1a)
(i) Poor safety training for workers
(ii) Lack of proper safety equipment
(iii) Failure to follow safety protocols
(iv) Unsafe working conditions
(1bi)
Trowel:
(Draw the diagram)

(1bii)
Bolster:
(Draw the diagram)
(1biii)
Spade:
(Draw the diagram)
(1biv)
Spirit level:
(Draw the diagram)
===========================
(2a)
(i) To assess the suitability of the site for construction
(ii) To investigate any potential hazards or risks in the area
(iii) To determine the soil and geological conditions of the site
(iv) To gather information necessary for the design and construction of the project
(2b)
(i) Bearing capacity of a soil: The bearing capacity of a soil refers to the maximum load that the soil can support without undergoing significant deformations or failure. It is an important factor to consider in construction projects to ensure that the soil can support the weight of structures like buildings, bridges, or roads.
(ii) Angle of repose of soil: The angle of repose is the steepest angle at which a pile of unconsolidated soil remains stable without collapsing or sliding. It is the natural angle formed by the soil particles due to gravity, and it varies depending on the characteristics of the soil.
(iii) Datum level: Datum level is a reference point or an arbitrary point used as a base elevation or starting point for measuring heights or depths in surveying, engineering, or construction projects. It serves as a common reference point for all measurements within a specific area.
(iv) Water table: The water table is the level at which the groundwater is found beneath the Earth’s surface. It is the boundary between the zone of saturation, where the spaces between soil particles are filled with water, and the zone of aeration, where the spaces are filled with air.
(v) Subsoil drainage: Subsoil drainage refers to the system of removing excess water from the soil below the ground surface. It helps to prevent waterlogging, improve soil structure, and promote healthy root growth in plants by controlling the water content within the soil profile.
(vi) Soil investigation: Soil investigation is the process of studying and analyzing the properties, composition, and behavior of soil at a particular site. It involves collecting soil samples, conducting tests to assess soil strength, stability, and other characteristics, and providing valuable information for various engineering and construction projects.
===========================
(3)
(Draw the diagram)
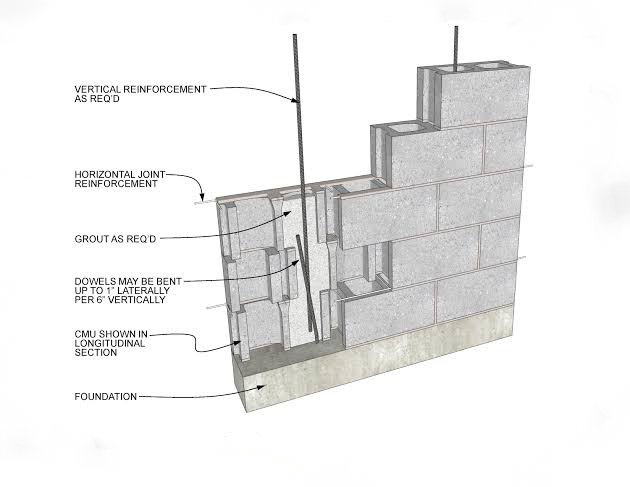
Continuous vertical joints in a wall can lead to significant risks of failure due to reduced structural stability and increased susceptibility to water infiltration. The lack of horizontal reinforcement in these joints can weaken the overall integrity of the wall, making it more prone to cracking and potential collapse. Water penetration through these joints can further exacerbate deterioration, causing issues such as mold growth and compromising the structural integrity over time.
===========================
(5)
Given:
Internal diameter of the sewer = 1000m
Thickness of brickwork = 225mm = 0.225m
Length of the sewer = 3000m
External diameter:
= 1000 + (2 x 0.225)
= 1000.45m
External radius = (1000.45)/2
= 500.225m
Internal radius = 1000/2
= 500m
Volume of the cylindrical shell:
= π x 3000 x (500.225² – 500²)
= π x 3000 x 225.50625
= 2127664.92m³
===========================
(6a)
(Draw the diagram)
(6b)
(i) Applying Non-Slip Tape: One common and cost-effective way to provide a non-slip surface to the treads of a stair is by applying non-slip tape. This adhesive-backed tape is typically made of a durable, textured material that enhances traction and reduces the likelihood of slipping.
(ii) Installing Non-Slip Stair Treads: Another approach is to install non-slip stair treads made of materials such as rubber, vinyl, or abrasive grit strips. These treads are designed to provide a secure footing and can be easily affixed to the existing treads.
(iii) Using Anti-Slip Paint or Coating: Applying anti-slip paint or coating to the stair treads is another effective way to enhance traction and prevent slipping. These coatings typically contain added texture or grit that improves grip and reduces the risk of accidents.
(iv) Incorporating Non-Slip Inserts: Non-slip inserts like metal or rubber strips can be embedded into the surface of the stair treads to create a non-slip surface. These inserts are often durable and offer long-lasting slip resistance.
===========================
(7a)
(i) Preparation of the Substrate: Before laying granolithic concrete, it is crucial to prepare the substrate properly. The substrate should be clean, free from any loose particles, and adequately compacted. Any existing coatings or dirt should be removed to ensure a good bond between the substrate and the concrete.
(ii) Mixing the Granolithic Concrete: Granolithic concrete is typically a mix of cement, sand, crushed rock or gravel, and sometimes a small amount of water-reducing admixture. The mix should be well-proportioned to achieve the desired strength and workability. It is important to mix the components thoroughly to ensure a homogeneous mixture.
(iii) Application and Spreading: Once the granolithic concrete mix is prepared, it is placed onto the prepared substrate. Workers then spread and compact the concrete mix using tools such as trowels, straightedges, and floats. Care should be taken to achieve a uniform layer thickness throughout the surface.
(iv) Finishing and Trowelling: After the concrete mix is spread evenly, it is trowelled to achieve a smooth and level surface. This process involves carefully working the surface with a trowel in circular or sweeping motions to remove any imperfections and create a dense finish. Additionally, edge forms can be used to create clean and sharp edges.
(v) Curing and Protection: Proper curing is essential to allow the granolithic concrete to develop its strength and durability. Curing methods can include covering the surface with wet burlap, plastic sheeting, or applying curing compounds. It is crucial to protect the freshly laid concrete from drying too quickly or being exposed to extreme weather conditions.
(vi) Jointing and Crack Control: Depending on the size of the area, joints may need to be cut into the concrete to control cracking. These joints can help accommodate any potential movement in the concrete due to temperature changes or other factors. Jointing should be done at regular intervals to prevent random cracking.
(vii) Surface Finishing: Once the granolithic concrete has cured sufficiently, the surface can be further finished as desired. This can include polishing, honing, or applying sealants to enhance the appearance and durability of the concrete surface.
(7b)
(i) Polyurethane finishes: These finishes are durable and resistant to chemicals, making them ideal for high-traffic areas. They provide a glossy sheen and excellent protection against scratches and stains.
(ii) Epoxy finishes: Epoxy coatings are tough and impact-resistant, commonly used in industrial settings due to their durability and ability to withstand heavy loads. They are also known for their seamless and easy-to-clean surface.
(iii) Acrylic finishes: Acrylic floor finishes offer a moderate level of durability and are available in various gloss levels. They are popular for their quick drying time and ease of application.
(iv) Vinyl finishes: Vinyl floor finishes provide a protective layer that enhances the durability of the underlying floor. They are known for their resistance to water and stains, making them suitable for areas prone to spills.
===========================
COMPLETED

Leave a Reply